Laboratory on Green Logistics
Scientific responsible: Pietro Evangelista
Abstract
Freight transport and logistics are essential for a country’s economic development, but at the same time they produce harmful externalities to the environment and human health mainly due to the significant contribution these activities make to harmful emissions. In this context, it is necessary for companies providing logistics and freight transport services together with manufacturing and commercial distribution companies to implement impactful strategies to decarbonise their activities along the entire supply chain. Green logistics is considered one of the most important levers to manage the supply chain in a sustainable way. However, the results of previous research show that in Italy sustainable logistics is poorly disseminated with a low propensity towards the adoption of sustainability programmes by Italian companies with particular reference to those providing freight transport and logistics services. Faced with this scenario in which there is a lack of systematic and continuous studies on this topic, the Laboratory on Green Logistics of the CNR-ISMed develop research aimed at raising awareness about the importance of sustainability in the sector and to spread the culture of green logistics as a driver of strategic business development to face the challenges posed by climate change. The main topics studied within the Laboratory concern decarbonisation strategies, environmental communication and reporting, and environmental collaboration in the supply chain. Other topics investigated are the contribution and role of digital technologies to support companies’ sustainability programmes, the reduction of the environmental impact of urban logistics, and the sustainability of logistics in rural areas.
Objectives
Freight transport and logistics play an important role in the economy and society as they make a significant contribution to a country’s gross domestic product (GDP) and have a strong impact on growth and employment. It is estimated that in many developed countries, freight transport and logistics account for between 6% and 12% of GDP. The value of all transport-related assets, including infrastructure and vehicles, can easily account for half of the GDP of an advanced economy. In terms of employment, the logistics services industry directly employs around 10 million people in the EU and accounts for around 5% of EU GDP. The value of the cost of logistics, including transport and warehousing, represents between 10% and 15% of the cost of a finished product for European companies. Efficient transport systems and logistics are crucial for European companies to compete effectively in the global economy.
However, logistics activities produce a number of negative externalities, many of which depend on the considerable amount of harmful emissions emitted by these activities. Despite improvements in transport technologies and fuels, emissions from the freight transport and logistics sector continue to grow both globally and regionally. Recent estimates indicate that greenhouse gas emissions from the sector worldwide amount to about 4,200 million tonnes CO2 which are equivalent to approximately 9 per cent of global emissions. Furthermore, forecasts up to 2050 show a significant increase in demand for freight transport that will result in a corresponding increase in greenhouse gas emissions.
Starting from this point, there has been a strong emphasis of all supply chain actors on reducing emissions and other negative externalities resulting from their activities. Therefore, the topic of green logistics has assumed considerable importance as an indispensable tool for managing the supply chain in a more sustainable way.
However, a series of studies conducted over the last few years have shown that in Italy the approach towards more sustainable logistics is not very widespread with little adoption of sustainability programmes by companies, with particular reference to companies providing logistics and freight transport services.
Faced with this scenario, the “Green Logistics Laboratory” of the CNR-ISMed develops research activities on the environmental sustainability in freight transport and logistics in order to disseminate the culture of sustainability in the sector and help companies develop strategies and actions to reduce their environmental impact and counteract the effects of climate change.
The specific objectives of the Laboratory are:
(i) to raise awareness among companies and key stakeholders about the environmental impact of freight transport and logistics;
ii) to produce analysis and research on key issues related to green logistics in Italy and disseminate the results;
(iii) design and provide solutions to companies facing the challenges of green logistics; and
(iv) contribute to the definition of policies to reduce the environmental impact of logistics and freight transport.
Activities
The Green Logistics Laboratory develops the following three different types of synergically connected activities:
1) Research: analysing the phenomenon of sustainable logistics in Italy through direct empirical qualitative-quantitative surveys and identifying ‘best practices’ to be transferred to companies. The results of this research are dissemination using different channels such as articles in international journals, papers presented at national and international conferences and workshops, teaching activities at Italian and foreign universities and collaborating with bodies and institutions responsible for developing policies in the transport and logistics sector;
2) Business services: produce studies on the de-carbonisation of business activities, based on the identification of the most suitable actions to reduce their environmental impact and help companies implement green logistics strategies;
3) Training: design and provide companies and organisations with training programmes to update staff skills and/or acquire new skills in the field of green logistics and combating climate change.
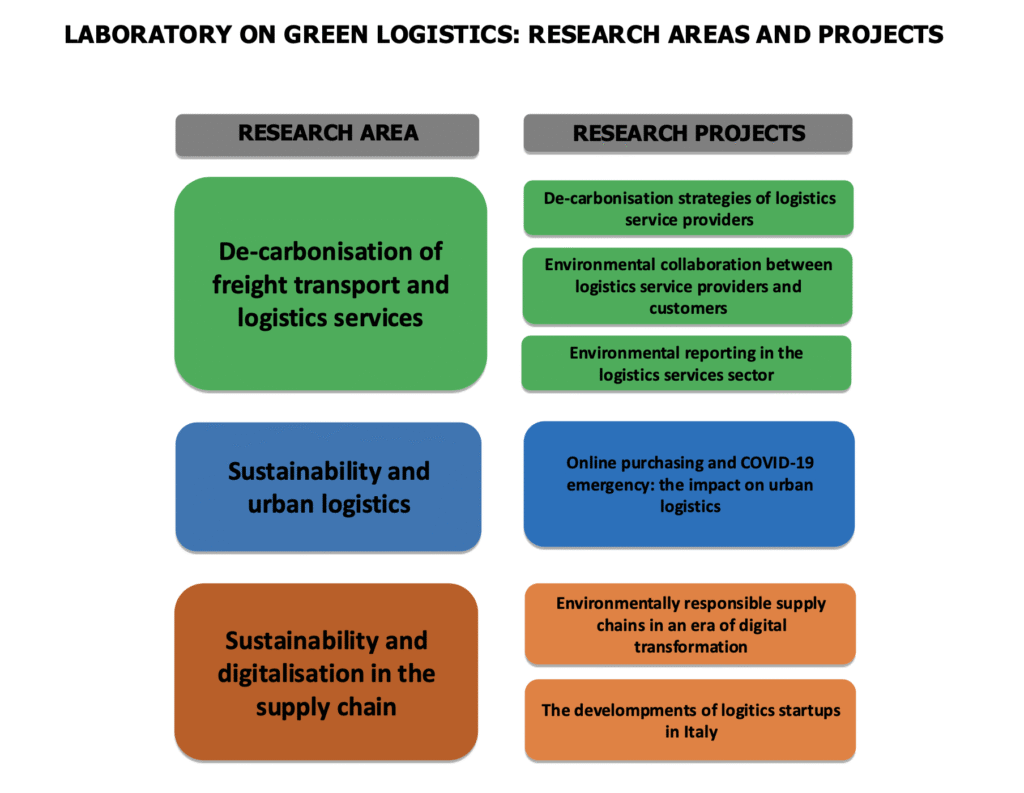
Research themes
The main research areas and related research themes/projects developed within the scope of the Green Logistics Laboratory’s activities are many and interrelated. They are summarised in the figure below:
Contacts and collaborations
The Laboratory on Sustainable Logistics is part of a very wide and structured network of contacts and collaborations including universities, research centres, companies and institutions both in Italy and abroad such as: Scuola Universitaria Superiore Sant’Anna di Pisa (Department of Management); Politecnico di Milano (School of Management); LUIC University Carlo Cattaneo (School of Industrial Engineering); Lappeenranta University of Technology – LUT (Business School), Finland; Wroclaw University of Economics and Business, – WUE (Department of Strategic Management and Logistics), Poland; Linköping University (Division of Logistics Management), Sweden; Heriot-Watt University (Logistics Research Centre), UK; Copenhagen Business School – CBS (Institute for Digitalisation), Denmark; University of Pau and the Pays de l’Adour (Center For Research and Studies in Management), France; Reykjavik University (Department of Business Administration), Iceland; Ibn Zohr University, Morocco; European Logistics Association (ELA); Logistics Research Network – LRN; Green Transition Hub; SOS-LOGistica, Association for Sustainable Logistics; International Purchasing and Supply Education and Research Association – IPSERA; World Conference on Transport Research Society – WCTRS; Italian Society of Transport and Logistics Economists – SIET.
Main research products
The Green Logistics Laboratory produces numerous products related to the research carried out. The main research products from the last two years are listed below:
– Creazza, A., Colicchia, C., Evangelista, P. (2023) Leveraging shippers-logistics providers relationships for better sustainability in logistics: the perspective of SMEs. International Journal of Logistics Management.
– Lo Storto, C., Evangelista, P., (2023) Infrastructure efficiency, service quality and environmental impact of land logistics systems in the EU: A DEA-based dynamic mapping, Research in Transportation Business and Management, Vol. 46, 100814.
– Kähkönen, A.-K., Evangelista, P., Hallikas, J., Immonen, M., Lintukangas, K. (2023) COVID-19 as a Trigger for Dynamic Capability Development and Supply Chain Resilience Improvement, International Journal of Production Research, Vol. 61, 2696-2715.
– Evangelista P., Hallikas J., Jaber M. (eds.) (2023) Environmentally Responsible Supply Chains in an era of Digital Transformation: Research Developments and Future Prospects, Edward Elgar Publishing Limited (UK).
– Evangelista, P., Hallikas, J. (2022) Exploring the influence of ICT on sustainability in supply management: evidence and directions for research, Cleaner Logistics and Supply Chain, Vol. 4, 100051.
– El Baz, J., Evangelista, P., Jebli, F., Iddik, S. (2022) Assessing green innovation in supply chain management research: A systematic review based on causal mechanisms framework, International Journal of Logistics Management, Vol. 33 (3), 1114-1145.
– Evangelista P., Kianto A., Hussinki H., Vanhala M., Nisula A.-M. (2023). Knowledge-based human resource management, logistics capability, and organizational performance in small Finnish logistics service providers, Logistics, 7, 12.
– Grant, D.B., Shaw, S., Sweeney, E., Bahr W. Chaisurayakarn, S., Evangelista P. (2023). Using mixed methods in logistics and supply chain management research – current status and future directions, International Journal of Logistics Management.
– Kiba-Janiak, M., Cheba, K., Mucowska M., Kelli Oliveira, L., Piecyk, M., Evangelista, P., Prockl, G., Rześny-Cieplińska, J. (2023). How to the design a Business Model for Sustainable Last-Mile Delivery and Returns from E-Customers’ Expectations Perspective? World Conference on Transport Research (WCTR), Montréal, Québec (Canada).
– Di Ruocco, I., Maggi, E., Evangelista, P. (2023) The role of parcel lockers for last-mile deliveries: A Systematic Literature Review, XXI Workshop Annuale della Società Italiana di Economia e Politica Industriale (SIEPI), Sessione speciale SIET – Società Italiana di Economia dei Trasporti e della Logistica, 15-16 Giugno 2023, Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II – Dipartimento di Scienze Politiche, Napoli.
– El Baz, J., Evangelista, P., Sweeney, E. (2023) A survey on unethical supply chain practices in conflict regions, 27th Annual Conference of Logistics Research Network 2023, 6-8 September, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh (UK).
– Evangelista, P., Hallikas, J., Jaber, M.Y. (2023) Digitalisation and Sustainable Supply Chain Management – Past Development and Future Significance, in Evangelista P., Hallikas J., Jaber M., (eds.) Environmentally Responsible Supply Chains in an era of Digital Transformation: Research Developments and Future Prospects, Edward Elgar Publishing Limited (UK).
– Hallikas, J., Evangelista, P., Lintukangas, K., Kähkönen, A.K., Immonen, M. (2023). Covid-19 Disruption Impacts on Supply Chains: An Empirical Exploration on Disruptions, Resiliency and Risk Management Strategies, in Omera Khan, Michael Huth, George A. Zsidisin and Michael Henke (2023) Supply Chain Resilience. Reconceptualizing Risk Management in a Post-Pandemic World, Springer.
– Evangelista, P., Hallikas, J. (2022) Exploring the influence of ICT on sustainability in supply management: evidence and directions for research, Cleaner Logistics and Supply Chain, Vol. 4, July 2022, 100051 (open access)
– El Baz, J., Evangelista, P., Jebli, F., Iddik, S., (2022) Assessing green innovation in supply chain management research: A systematic review based on causal mechanisms framework, International Journal of Logistics Management, Vol. 33 No. 3, pp. 1114-1145. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJLM-07-2021-0354
– Evangelista, P., Hallikas, J., (2022) Assessing the relationship between digital technologies and sustainable supply chain management through a systematic literature review, International Working Seminar on Production Economics 2022, February 21-25, 2022, Innsbruck, Austria.
– Evangelista P., Bosone M. Testa F. (2022) How COVID-19 has changed the online consumer behaviours. Implications for sustainable last mile deliveries in the Italian e-commerce market, 5th International Conference Green Cities 2022 – Green Logistics for Greener Cities, 16-17 May 2022, Szczecin, Poland.
– Colicchia C., Creazza A., Evangelista P. (2022) Leveraging Shippers-Logistics Providers Relationships for Better Sustainability in Logistics: the perspective of SMEs, 17th CSCMP European Research Seminar (ERS) on Logistics and SCM. 20-21 June, Politecnico di Milano (Italy).
– Sweeney E., Shaw S., Grant D., Evangelista P., Chaisurayakarn S. (2022) Using Mixed Methods in Logistics and Supply Chain Management Research – current state and future directions, 26th Annual Conference of Logistics Research Network 2022 “Supply Chain Innovation: People, Process, Technology”, 7-9 September, Aston University (UK).
Last update
17 April 2025, 13:19

 CNR – ISMed
CNR – ISMed